Lead
Basic Facts about Lead :
Lead, element symbol pb is a soft, dull silvery white or greyish metal very malleable, ductile, and dense and is a poor conductor of electricity. The symbol Pb is an abbreviation of the Latin word for lead, plumbum. It belongs to the carbon family of elements. It is very resistant to corrosion but tarnishes upon exposure to air. Lead isotopes are the end products of each of the three series of naturally occurring radioactive elements. Known in antiquity and believed to be the oldest of metals, lead is highly durable and resistant to decaying, as the continuous use of lead water pipes installed by the ancient Romans.
Lead is mentioned often in early biblical accounts. The Babylonians used the lead metal as plates on which they recorded inscriptions. The Romans used it for tablets, water pipes, coins, and even cooking utensils.
On a weight basis, lead has nearly the same abundance in Earth’s crust as tin. Tin and lead shared very similar properties so, for a long time both were considered as different forms of same metal.
Though lead is not abundant, natural concentration processes have resulted in substantial deposits of commercial significance. Rarely found free in nature, lead is present in several minerals, but all are of minor significance except the sulphide, PbS (galena, or lead glance), which is the major source of lead production throughout the world
Native lead is rare in nature. Currently lead is usually found in ore with zinc, silver and copper and it is extracted together with these metals. The main lead mineral is found in Galena (PbS) and there are also deposits of cerrussite and anglesite which are mined.
MORE FACTS ABOUT LEAD
Lead occurs naturally in the environment. However, most lead concentrations that are found in the environment are a result of human activities. In car engines lead is burned, giving birth to lead salts (chlorines, bromines, oxides). These lead salts enter the environment through the exhausts of cars. The larger particles drop to the ground immediately and pollute soils or water surfaces, the smaller particles travel long distances through air and remain in the atmosphere. Part of this lead falls back on earth when it is raining. This lead-cycle caused by human production is much more extended than the natural lead-cycle. It has caused lead pollution to be a worldwide issue.
Lead is highly toxic and effects our central nervous system and also our ecosystem. It is harmful for babies and the young ones.
Lead is the only metal which shows zero Thomson effect. It means that when the electricity is passed through lead, heat is neither at absorbed nor released.
Except in powder form lead is not as reactive as other metals. Lead is a post –transition metal. It shows weak or low metallic character, often creating covalent bonds with other elements.
Pencil lead is actually graphite form of carbon, it is always misunderstood as lead.
Lead Atomic Data
| Atomic number | 82 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Volume | 18.3 cc/mol |
| Atomic Radius | 175 pm |
| Atomic mass | 207.2 g.mol-1 |
| Electronegativity according to Pauling | 1.8 |
| Density | 11.34 g.cm-3 at 20°C |
| Melting point | 327 °C |
| Boiling point | 1755 °C |
| Vander Waals radius | 0.154 nm |
| Ionic radius | 0.132 nm (+2) ; 0.084 nm (+4) |
| Isotopes | 13 |
| Covalent radius | 147 pm |
| Oxidation state | 4 , 2 |
| Evaporation heat | 177.8 kj/mol |
| Fusion heat | 4.77 kj/mol |
| First ionizing energy | 715.2 kj/mol |
| Debye temperature | 88.00 °K |
| Lattice constant | 4.950 Å |
| Specific heat (@20°CJ/ g.mol) | 0.159 |
Applications :
- Lead pipes bearing the insignia of Roman emperors, used as drains and water pipes are still in service. Alloys include pewter and solder. Tetraethyl lead (PbEt4) is still used in some grades of petrol (gasoline) but is being phased out on the environmental ground.
- Lead is a major constituent of the lead-acid battery used extensively in car batteries.
- It is used as a pigment in ceramic glazes and potteries.
- It is used in paints or other protective coatings.
- It is the base metal for organ pipes, and it is used as electrodes in the process of electrolysis.
- It is majorly used in the glass of computer and television screens, to shield and protect the viewer from radiation.
- Other uses are in sheeting, cables, solders, lead crystal glassware, ammunitions, bullets, bearings, as weights in sport equipment, lead crystal glass, roofing and statues.
- It is used to store corrosive liquids.
- It is a sound and vibration absorber too. It is used in radiation shielding in medical analysis and video display equipment’s.
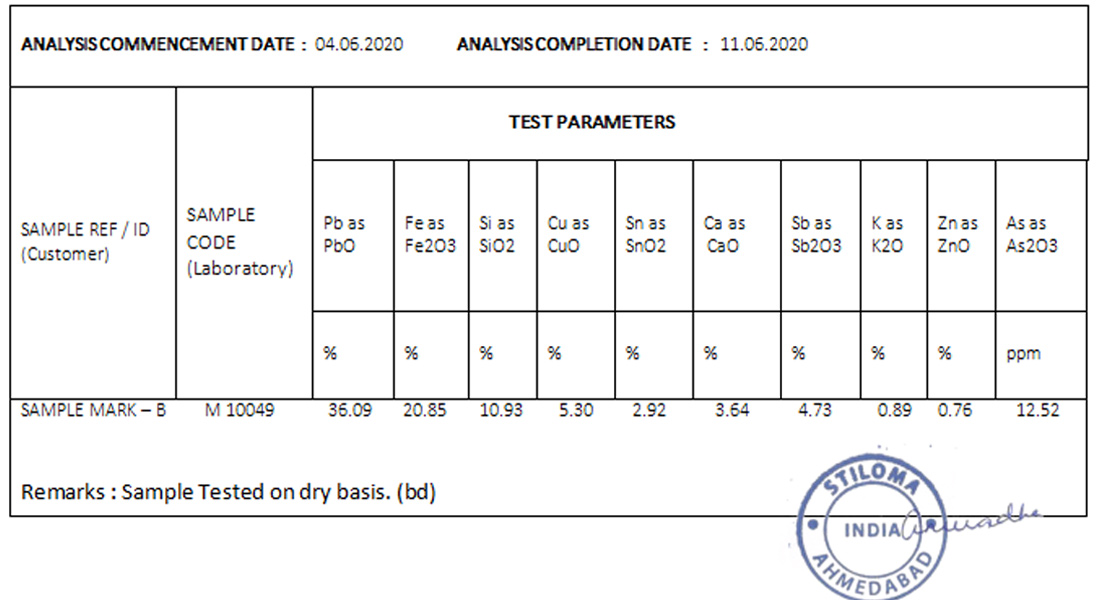
Test Report :
| SAMPLE PARTICULARS | LEAD POWDER |
|---|---|
| PARAMETERS TESTED | (Zn, Cu, Si, Sn, Sb, Zn, As, Ca, & Fe on (DB) |
| TEST METHOD | (Zn, Cu, Sn, As, Ca, & Sb) – by AAS, Fe Wet Chemical Method, Pb, - By IBM, Si –By GravimetricMethod K – By Flame Photometer |
Test Report :